Facile synthesis of boronic acid-decorated carbon nanodots as optical nanoprobes for glycoprotein sensing†
Abstract
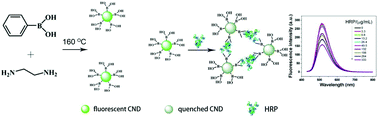
In this article, we proposed new nitrogen-doped boronic acid-decorated carbon nanodots (CNDs) for the recognition and detection of glycoproteins. These doped, decorated CNDs were obtained by a one-step hydrothermal carbonization method using phenylboronic acid and ethylenediamine as precursors. Compared to traditional synthesized and then functionalized nanoscale sensing systems, this method is more facile and efficient. The as-prepared nitrogen-doped CNDs possessed a quasi-spherical morphology and a high quantum yield of approximately 14.5%. The added glycoproteins (taking horseradish peroxidase as a model protein) can selectively induce the assembly and fluorescence quenching of CNDs through the formation of cyclic boronate esters, because the boronic acid groups on the CND surfaces can covalently interact with cis-diol-containing glycoproteins. These fluorescence responses can be used to properly quantify horseradish peroxidase in the range of 3.3–333.3 μg mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.52 μg mL−1, and the selectivity assay with functionalized CNDs was further investigated using various proteins with different quantities of glycosylation sites as well as using smaller molecules. The results show that the nanosensing system possesses favorable selectivity. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, the system has great application prospects as a practical platform for glycoprotein sensing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...