Fluorescence based detection of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in water using hydrophobic interactions†
Abstract
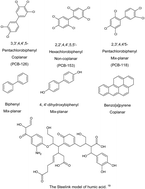
Despite increasing controls in their production and disposal, persistent organic pollutants in water, even at concentrations below parts per million, represent an ongoing environmental health risk. Despite this concern, the detection of these compounds in water sources rely upon expensive, time consuming approaches that do not permit frequent monitoring and evaluation. In this work, a new fluorescence-based technique is presented for the detection of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in water. Benzopyrene (BaP) fluorescence was shown to increase with trace concentrations of aromatic organic pollutants. BaP forms a hydrophobic complex with PCBs, which has allowed for the successful detection of pollutants including PCB-126, PCB-153 and PCB-118. To determine the selectivity and robustness of this response, the impact of pH, ionic strength and humic acid to mimic surface water conditions is explored. While suppression of the signal was seen, these factors’ impact on the detection of PCBs was minor, suggesting that a potential sensing strategy can be developed through this interaction. It is seen that the number and location of chlorine atoms are important along with the geometric orientation of molecule's structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...