Synthesis, photophysical properties and surface chemistry of chalcopyrite-type semiconductor nanocrystals
Abstract
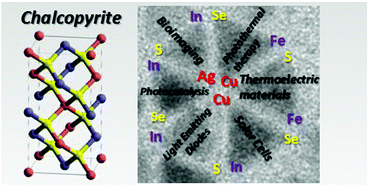
Ternary and quaternary chalcopyrite-type nanocrystals of MIMIIIE2 and MIMIIIZnE2 type (MI = Ag, Cu; MIII = In, Fe; E = S, Se) and their core/shell structures have attracted a huge interest in the past decade because they combine size- and composition-tunable optical and electronic properties without relying on toxic elements such as Cd and Pb. These materials had been primarily studied as light harvesters in solar cell applications. However, in the form of colloidal nanocrystals, they exhibit remarkable photoluminescence properties in the visible and near infrared range. At the same time, the underlying emission mechanisms are distinctly different from those occurring in binary semiconductor quantum dots. Several models have been developed to explain the origin of the observed phenomena, in particular the line width broadening, large Stokes shifts and long photoluminescence lifetimes. This review first focusses on the current understanding of the optical properties of the title compounds. Next, an overview of the main synthesis methods is given, both in organic solvents and in the aqueous phase. In the second part, the surface chemistry and ligand exchange procedures are discussed. Finally, organic/inorganic hybrids of chalcopyrite nanocrystals with electroactive molecules are presented as well as their use in photovoltaics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...