Enhanced electrochromic performances and patterning of Ni–Sn oxide films prepared by a photosensitive sol–gel method
Abstract
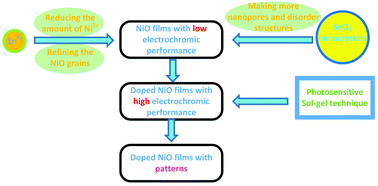
Herein, we report Sn4+ doped Ni–Sn oxide based electrochromic patterned films for high performance display using a new method that combines a photochemical etching technique with a sol–gel method. The patterning of the films was advanced to the gel film preparation stage by exploiting the ultraviolet photosensitivity of Ni–Sn precursor sols, thereby effectively avoiding damage to the electrochromic performance of the films during the etching process involved in traditional patterning techniques such as dry etching, wet etching, etc. The contents of Sn4+ ions, SnO2 nanocrystals, and NiO nanocrystals in the films were controlled by adjusting the molar ratio of Sn : Ni in the photosensitive sol. The modifications of the chemical state and microstructure of NiO by Sn4+ ions and SnO2 nanocrystals effectively promoted the formation of active substances (Ni3+ conversion to Ni2+) and nano-channels for ion (such as OH−) transportation, thereby enhancing the electrochromic properties of NiO films. At a Sn : Ni molar ratio of 0.2 : 1, the films achieved the strongest electrochromic performances with an optical modulation of 70% at 550 nm, switching times of 5 s (coloring) and 4 s (bleaching), and a coloration efficiency of 52 cm2 C−1. The performance of the film remained unchanged even after 2000 coloring–bleaching cycles. Based on the experimental results, we conclude that the Ni–Sn oxide patterned films obtained by co-doping Sn4+ ions and SnO2 nanocrystals show potential for application in large display fields such as billboards and indicator boards.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...