Design of salt-responsive and regenerative antibacterial polymer brushes with integrated bacterial resistance, killing, and release properties†
Abstract
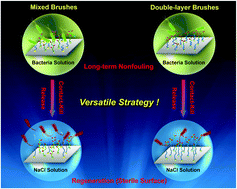
The development of smart materials and surfaces with multiple antibacterial actions is of great importance for both fundamental research and practical applications, but this has proved to be extremely challenging. In this work, we proposed to integrate salt-responsive polyDVBAPS (poly(3-(dimethyl(4-vinylbenzyl) ammonio)propyl sulfonate)), antifouling polyHEAA (poly(N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide)), and bactericidal TCS (triclosan) into single surfaces by polymerizing and grafting polyDVBAPS and polyHEAA onto the substrate in a different way to form two types of polyDVBAPS/poly(HEAA-g-TCS) and poly(DVBAPS-b-HEAA-g-TCS) brushes with different hierarchical structures, as confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), atom force microscopy (AFM), and ellipsometry. Both types of polymer brushes demonstrated their tri-functional antibacterial activity to resist bacterial attachment by polyHEAA, to release ∼90% of dead bacteria from the surface by polyDVBAPS, and to kill ∼90% of bacteria on the surface by TCS. Comparative studies also showed that removal of any component from polyDVBAPS/poly(HEAA-g-TCS) and poly(DVBAPS-b-HEAA-g-TCS) compromised the overall antibacterial performance, further supporting a synergistic effect of the three compatible components. More importantly, the presence of salt-responsive polyDVBAPS allowed both brushes to regenerate with almost unaffected antibacterial capacity for reuse in multiple kill-and-release cycles. The tri-functional antibacterial surfaces present a promising design strategy for further developing next-generation antibacterial materials and coatings for antibacterial applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...