Photocrosslinked acemannan-based 3D matrices for in vitro cell culture†
Abstract
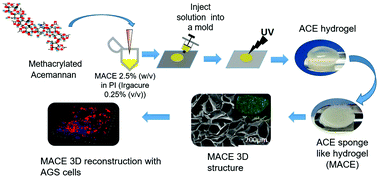
Current biomedical research has highlighted the potential use of medicinal plant derivatives as advanced suitable biomaterials due to their biological properties. Acemannan (ACE) is the main polysaccharide of Aloe vera (AV) leaves with many reported biological properties, including immunomodulatory activity, antibacterial action, wound healing induction, and cytocompatibility. These properties suggest that ACE is an appealing material for the development of 3D structures for biomedical purposes. In this study, ACE was modified by a methacrylation reaction using methacrylic anhydride. Further 3D sponges were developed by processing modified ACE by photocrosslinking using UV irradiation and the freeze-drying technique. Both FTIR and 1H NMR spectroscopy confirmed the effectiveness of the functionalization. SEM and μ-CT revealed that the cross-sections of the methacrylated acemannan (MACE) sponges have open macropores and a narrow pore size distribution within them. We hypothesized that the intrinsic features of ACE could enhance tumor growth, mimicking the biological tumor microenvironment. Therefore, gastric cancer cells (AGS cell line) were cultured in contact with these matrices for up to 14 days to evaluate their cytocompatibility as a processed biomaterial. Results obtained by live-dead assay and MTS showed that cells are viable and metabolically active. Furthermore, confocal laser scanning microscopy analysis showed a homogeneous distribution of cells within the sponge. Therefore, the photocrosslinking on acemmann is proposed as an alternative approach that could significantly improve the processability of acemannan, allowing the production of high added-value structures enabling exploitation of its potential biomedical value.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...