Ultrapermeable graphene oxide membranes with tunable interlayer distances via vein-like supramolecular dendrimers†
Abstract
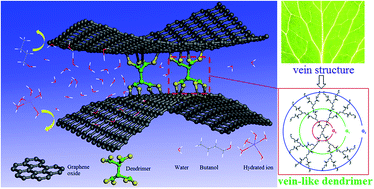
Graphene oxide (GO) membranes display fascinating properties in molecular and ionic separation. The interlayer distance between adjacent GO nanosheets determines the separation efficiency. Currently, the interlayer distance is mostly tuned using small molecule or polymer crosslinkers, which often lead to a relatively low permeation flux due to the considerable channel occupancy. Inspired by the vein structure in nature, we propose a strategy of using vein-like supramolecular dendrimers as crosslinkers to tune the interlayer distance of GO membranes. We chose primary amine-terminated polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers with a medium molecular weight, a regularly branched structure and multiple peripheral amine groups. At a low adding amount (4 wt% PAMAM Generation 0 and equal molar of Generation 1 and 2) of dendrimers, the interlayer distance can be tuned in the range of 0.43–0.76 nm in the wet state. The resulting GO-based membranes exhibited a permeation flux of 124 kg m−2 h−1 and a NaCl rejection rate of >99.99% in simulated seawater desalination, as well as a permeation flux of 9108 g m−2 h−1 and a separation factor of 2941 in butanol dehydration, far beyond the performance of state-of-the-art membrane counterparts. Moreover, the membrane remains stable for 168 h and exhibits outstanding mechanical stability. Our study provides a novel avenue to robust and high-performance 2D nanosheet separation membranes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...