Dilute solution structure of bottlebrush polymers†
Abstract
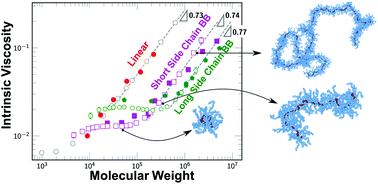
Bottlebrush polymers are a class of macromolecules that have recently found use in a wide variety of materials, ranging from lubricating brushes and nanostructured coatings to elastomeric gels that exhibit structural colors. These polymers are characterized by dense branches extending from a central backbone and thus have properties distinct from linear polymers. It remains a challenge to specifically understand conformational properties of these molecules, due to the wide range of architectural parameters that can be present in a system, and thus there is a need to accurately characterize and model these molecules. In this paper, we use a combination of viscometry, light scattering, and computer simulations to gain insight into the conformational properties of dilute solution bottlebrush polymers. We focus on a series of model bottlebrushes consisting of a poly(norbornene) (PNB) backbone with poly(lactic acid) (PLA) side chains. We demonstrate that intrinsic viscosity and hydrodynamic radius are experimental observations sensitive to molecular architecture, exhibiting distinct differences with different choices of branches and backbone lengths. Informed by the atomistic structure of this PNB–PLA system, we rationalize a coarse-grained simulation model that we evaluate using a combination of Brownian dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations. We show that this exhibits quantitative matching to experimental results, enabling us to characterize the overall shape of the bottlebrush via a number of metrics that can be extended to more general bottlebrush architectures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...