Methanesulfonic acid-based electrode-decoupled vanadium–cerium redox flow battery exhibits significantly improved capacity and cycle life†
Abstract
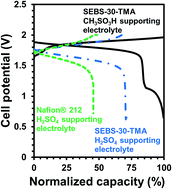
An electrode-decoupled V–Ce redox flow battery (ED-RFB) was developed with 40% greater theoretical volumetric capacity and a 30% enhancement in practical volumetric capacity was demonstrated. The use of methanesulfonic acid supported V and Ce electrolytes and a highly permselective polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene (SEBS) triblock copolymer anion exchange separator enabled a >95% reduction in capacity fade compared to standard H2SO4 supported V–Ce ED-RFBs. The methanesulfonic acid supported V and Ce electrolytes was examined using the Marcus–Hush kinetic formulation and the presence of strongly solvated cations was shown to reduce capacity fade by cation cross-over. The ED-RFB maintained nearly 100% coulombic efficiency (CE) and ca. 70% energy efficiency (EE) (at a 50 mA cm−2 galvanostatic charge/discharge current) over 100 cycles. The EE ranged from 85% at 25 mA cm−2 to 50% at 100 mA cm−2. The separator was highly acid stable with no changes in its FT-IR spectra and ionic conductivity before and after cycling. Thus, a V–Ce ED-RFB with long life, excellent rate capability and stability is demonstrated. The use of CH3SO3H, a “green” chemical with low toxicity and easy effluent treatment, facilitates scale-up and grid-scale deployment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
