Assessment of toxicity reduction in ZnS substituted CdS:P3HT bulk heterojunction solar cells fabricated using a single-source precursor deposition
Abstract
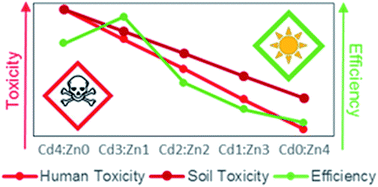
Utilisation of cadmium sulphide (CdS) for the preparation of hybrid bulk heterojunction (BHJ) solar cells is limited due to its high human, soil and marine toxicity. This work aims to reduce the toxicity of the cadmium based hybrid bulk heterojunctions, by varying the composition of metal sulphide nanoparticles between CdS and zinc sulphide (ZnS). Furthermore, these devices were created using a single-source precursor, which limits potential barriers for scaling up this process to industrial scale. It was found that the chemical composition of fabricated devices varied as expected; however, comparable morphologies were noted by SEM analyses. Toxicity of fabricated photovoltaic devices was estimated according to the life cycle assessment methodology, using the SimaPro software. Although negligible changes between the band gaps of prepared devices were calculated by decreasing the Cd load to 50 wt%, over 50% reduction to human toxicity could be achieved. As a photovoltaic device, the highest power conversion efficiency (0.018%) was observed for the device containing 75 wt% Cd and 25 wt% Zn, which also showed significant reductions for human and environmental toxicity (25% and 19% reduction, respectively) in comparison to the device containing only CdS, while increasing the power conversion efficiency by roughly 30%. It was also noted that although the ZnS only device had the lowest efficiency (0.002%, a decrease of roughly 98%), however, this allowed for a 99% reduction in human toxicity and a 73% reduction in terrestrial ecotoxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...