The influence of covalent and non-covalent functionalization of GNP based nanofluids on its thermophysical, rheological and suspension stability properties
Abstract
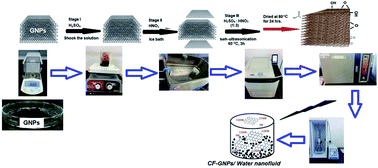
Covalent functionalization (CF-GNPs) and non-covalent functionalization (NCF-GNPs) approaches were applied to prepare graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs). The impact of using four surfactants (SDS, CTAB, Tween-80, and Triton X-100) was studied with four test times (15, 30, 60, and 90 min) and four weight concentrations. The stable thermal conductivity and viscosity were measured as a function of temperature. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy verified the fundamental efficient and stable CF. Several techniques, such as dispersion of particle size, FESEM, FETEM, EDX, zeta potential, and UV-vis spectrophotometry, were employed to characterize both the dispersion stability and morphology of functionalized materials. At ultrasonic test time, the highest stability of nanofluids was achieved at 60 min. As a result, the thermal conductivity displayed by CF-GNPs was higher than NCF-GNPs and distilled water. In conclusion, the improvement in thermal conductivity and stability displayed by CF-GNPs was higher than those of NCF-GNPs, while the lowest viscosity was 8% higher than distilled water, and the best thermal conductivity improvement was recorded at 29.2%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...