Highly reactive energetic films by pre-stressing nano-aluminum particles†
Abstract
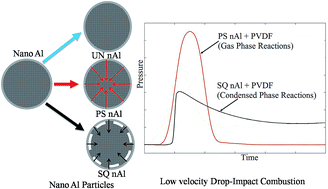
Energetic films were synthesized using stress altered nano-aluminum particles (nAl). The nAl powder was pre-stressed to examine how modified mechanical properties of the fuel particles influenced film reactivity. Pre-stressing conditions varied by quenching rate. Slow and rapid quenching rates induced elevated dilatational strain within the nAl particles that was measured using synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD). An analytical model for stress and strain in a nAl core–Al2O3 shell particle that includes creep in the shell and delamination at the core–shell boundary, was developed and used for interpretation of strain measurements. Results show rapid quenching induced 81% delamination at the particle core–shell interface also observed with Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). Slower quenching elevated dilatational strain without delamination. All films were prepared at approximately a 75 : 25 Al : poly(vinylidene fluoride) PVDF weight ratio and were 1 mm thick. A drop weight impact test was performed to assess ignition sensitivity and combustion. Stress altered nAl exhibited greater energy release rates and more complete combustion than untreated nAl, but reaction dynamics and kinetics proceeded in two different ways depending on the nAl quenching rate during pre-stressing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...