Notoamide-type alkaloid induced apoptosis and autophagy via a P38/JNK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells†
Abstract
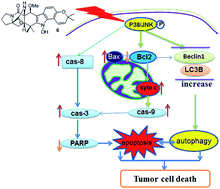
Bioassay-guided fractionation of a coral-associated fungus Aspergillus ochraceus LZDX-32-15 resulted in the isolation of eleven notoamide-type alkaloids, including four new congeners, namely notoamides W-Z (1–4). The structures of the new alkaloids were determined by extensive analyses of spectroscopic data (1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS), while ECD data were used for the configurational assignment. Three alkaloids (6, 10, 11) exerted potent inhibition against a panel of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 0.42 to 3.39 μM, that are comparable to the data for paclitaxel. Notoamide G (6) inhibited the viability of HepG2 and Huh-7 cells via both apoptosis and autophagy pathways. Notoamide G activated the expression of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9, in association with the degradation of the downstream gene PARP in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that notoamide G induced apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway and a dead receptor-mediated pathway. In addition, notoamide G increased the autophagic vacuole in both HepG2 and Huh-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner after 24 h through the significant upregulation of the key proteins Beclin1 and LC3B. Further investigation revealed that notoamide G promoted P38 and JNK phosphorylation, whereas the total protein of P-38 and JNK was slightly influenced. Accordingly, the antitumor proliferation of notoamide G in HCC cells was mechanistically mediated by apoptosis and autophagy through a P38/JNK signaling pathway, while notoamide G was considered as a potent lead for further development as an antitumor agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...