A comparative performance analysis of stand-alone, off-grid solar-powered sodium hypochlorite generators†
Abstract
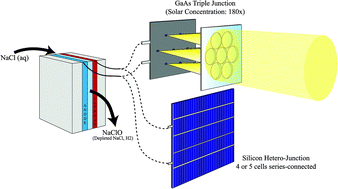
Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is a chemical commodity widely employed as a disinfection agent in water treatment applications. Its production commonly follows electrochemical routes in an undivided reactor. Powering the process with photovoltaic (PV) electricity holds the potential to install stand-alone, independent generators and reduce the NaClO production cost. This study reports the comparative assessment of autonomous, solar-powered sodium hypochlorite generators employing different photovoltaic (PV) technologies: silicon hetero-junction (SHJ) and multi-junction (MJ) solar cells. For Si hetero-junctions, the series connection of either four or five SHJ (4SHJ and 5SHJ, respectively) cells was implemented to obtain the reaction potential required. MJ cells were illuminated by a novel planar solar concentrator that guarantees solar tracking with minimal linear displacements. The three solar-hypochlorite generators were tested under real atmospheric conditions, demonstrating solar-to-chemical conversion efficiencies (SCE) of 9.8% for 4SHJ, 14.2% for 5SHJ and 25.1% for MJ solar cells, respectively. Simulations based on weather databases allowed us to assess efficiencies throughout the entire model year and resulted in specific sodium hypochlorite yearly production rates between 7.2–28 gNaClO cm−2 (referred to the PV surface), depending on the considered PV technology, location, and deployment of electronics converters. The economic viability and competitiveness of solar hypochlorite generators have been investigated and compared with an analog disinfection system deploying ultraviolet lamps. Our study demonstrates the feasibility of off-grid, solar-hypochlorite generators, and points towards the implementation of SHJ solar cells as a reliable technology for stand-alone solar-chemical devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...