Versatile functionalization of polymer nanoparticles with carbonate groups via hydroxyurethane linkages†
Abstract
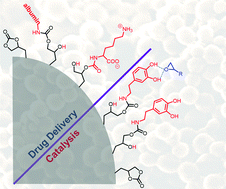
Synthesis of polymer nanoparticles bearing pendant cyclic carbonate moieties is carried out to explore their potential as versatile supports for biomedical applications and catalysis. Nanoparticles are produced by copolymerizing glycerol carbonate methacrylate with methyl methacrylate by the miniemulsion process. The ability of the nanoparticles to serve as carriers for biomolecules was studied by reacting them with various amines, amino acids, and proteins. The functionalized nanoparticles are systematically analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, solid state (SS) NMR spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Model studies are performed to investigate the reactivity of amino acids and albumin with the pendant carbonate groups. Functionalization of the nanoparticles with dopamine led to surface coverage with catechol groups as efficient heterogeneous hydrogen bond donors for the cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides under atmospheric pressure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...