Laser flash photolysis study of the photoinduced oxidation of 4-(dimethylamino)benzonitrile (DMABN)†
Abstract
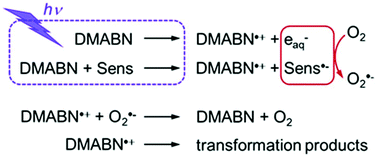
Aromatic amines are aquatic contaminants for which phototransformation in surface waters can be induced by excited triplet states of dissolved organic matter (3DOM*). The first reaction step is assumed to consist of a one-electron oxidation process of the amine to produce its radical cation. In this paper, we present laser flash photolysis investigations aimed at characterizing the photoinduced, aqueous phase one-electron oxidation of 4-(dimethylamino)benzonitrile (DMABN) as a representative of this contaminant class. The production of the radical cation of DMABN (DMABN˙+) after direct photoexcitation of DMABN at 266 nm was confirmed in accord with previous experimental results. Moreover, DMABN˙+ was shown to be produced from the reactions of several excited triplet photosensitizers (carbonyl compounds) with DMABN. Second-order rate constants for the quenching of the excited triplet states by DMABN were determined to fall in the range of 3 × 107–5 × 109 M−1 s−1, and their variation was interpreted in terms of electron transfer theory using a Rehm–Weller relationship. The decay kinetics of DMABN˙+ in the presence of oxygen was dominated by a second-order component attributed to its reaction with the superoxide radical anion (O2˙−). The first-order rate constant for the transformation of DMABN˙+ leading to photodegradation of DMABN was estimated not to exceed ≈5 × 103 s−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...