Production of a photohexapeptide library from entomopathogenic Photorhabdus asymbiotica PB68.1†
Abstract
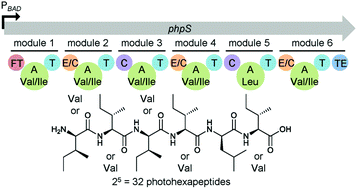
A new natural product compound library, photohexapeptide library, was identified from entomopathogenic Photorhabdus asymbiotica PB68.1 after the NRPS-encoding gene phpS was activated via promoter exchange. Peptide structures, including the absolute configurations of amino acids, were determined by using a combination of bioinformatics analysis and isotopic labelling experiments followed by detailed HPLC-MS analysis. Additionally, their structures were confirmed by chemical synthesis and NMR after preparative isolation. The chemical diversity of the photohexapeptides results from promiscuous adenylation domain specificity being an excellent example of how to create libraries in nature.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...