Nontoxic amphiphilic carbon dots as promising drug nanocarriers across the blood–brain barrier and inhibitors of β-amyloid†
Abstract
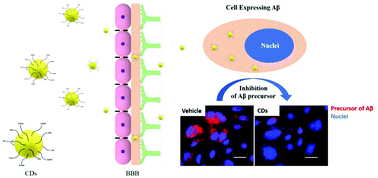
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a main obstacle for drug delivery targeting the central nervous system (CNS) and treating Alzheimer's disease (AD). In order to enhance the efficiency of drug delivery without harming the BBB integrity, nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery has become a popular therapeutic strategy. Carbon dots (CDs) are one of the most promising and novel nanocarriers. In this study, amphiphilic yellow-emissive CDs (Y-CDs) were synthesized with an ultrasonication-mediated methodology using citric acid and o-phenylenediamine with a size of 3 nm that emit an excitation-independent yellow photoluminescence (PL). The content of primary amine and carboxyl groups on CDs was measured as 6.12 × 10−5 and 8.13 × 10−3 mmol mg−1, respectively, indicating the potential for small-molecule drug loading through bioconjugation. Confocal image analyses revealed that Y-CDs crossed the BBB of 5-day old wild-type zebrafish, most probably by passive diffusion due to the amphiphilicity of Y-CDs. And the amphiphilicity and BBB penetration ability didn't change when Y-CDs were coated with different hydrophilic molecules. Furthermore, Y-CDs were observed to enter cells to inhibit the overexpression of human amyloid precursor protein (APP) and β-amyloid (Aβ) which is a major factor responsible for AD pathology. Therefore, data suggest that Y-CDs have a great potential as nontoxic nanocarriers for drug delivery towards the CNS as well as a promising inhibiting agent of Aβ-related pathology of the AD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...