Camptothecin-based dendrimersomes for gene delivery and redox-responsive drug delivery to cancer cells†
Abstract
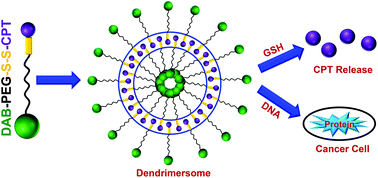
Combination therapy involving chemotherapeutic drugs and genes is emerging as a promising strategy to provide a synergistic therapeutic effect, to overcome drug resistance while reducing the severe side effects associated with conventional chemotherapeutic drugs. However, the lack of nanomedicines able to simultaneously carry anti-cancer drugs and nucleic acids limits the application of this therapeutic strategy. To overcome this issue, we proposed to synthesize a pro-drug dendrimer by conjugating the PEGylated, positively charged generation 3-diaminobutyric polypropylenimine dendrimer to the anti-cancer drug camptothecin with a redox-sensitive disulphide linkage, and evaluate its efficacy to co-deliver the complexed DNA and camptothecin to cancer cells. This PEGylated pro-drug dendrimer was found to spontaneously self-assemble into cationic (∼3–5 mV) vesicles at pH 7.4, at a critical aggregation concentration of about 200 μg mL−1. These vesicles (dendrimersomes) became smaller (150–200 nm) with increasing dendrimer concentration and remained stable over 7 days. They were able to release about 70% of the conjugated camptothecin in presence of 50 mM glutathione (equivalent to the intracellular environment of tumor tissue). They could also condense more than 85% of the DNA at dendrimer : DNA weight ratios of 5 : 1 and higher. DNA condensation occurred instantly and was found to be stable for at least 24 h. This led to an enhanced cellular uptake of DNA (by up to 1.6-fold) and increased gene transfection (by up to 2.4-fold) in prostate cancer cells in comparison with the unmodified dendrimer. These novel dendrimersomes are therefore promising for single carrier-based combination cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...