Development of multi-drug loaded PEGylated nanodiamonds to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in genetically engineered mouse models of pancreatic cancer†
Abstract
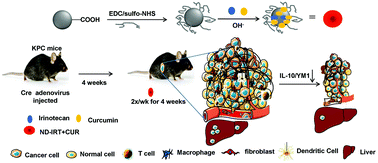
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a devastating disease. Nanomedicine, however, offers new opportunities to facilitate drug delivery in PDAC. Our previous work has shown that poly(ethylene glycol)-functionalized nanodiamond (ND) mediated drug delivery offered a considerable improvement over free drug in PDAC. Inspired by this result and guided by molecular simulations, we opted for simultaneous loading of irinotecan and curcumin in ultra-small PEGylated NDs (ND-IRT + CUR). We observed that ND-IRT + CUR was more efficacious in killing AsPC-1 and PANC-1 cells than NDs with single drugs. Using NDs functionalized with a near-infrared (NIR) dye, we demonstrated the preferential localization of the NDs in tumors and metastatic lesions. We further demonstrate that ND-IRT + CUR is capable of producing pronounced anti-tumor effects in two different clinically relevant, immune-competent genetic models of PDAC. Cytokine profiling indicated that NDs with or without drugs downregulated the expression of IL-10, a key modulator of the tumor microenvironment. Thus, using a combination of in silico, in vitro, and in vivo approaches, we show for the first time the remarkable anti-tumor efficacy of PEGylated NDs carrying a dual payload of irinotecan plus curcumin. These results highlight the potential use of such nano-carriers in the treatment of patients with pancreatic cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...