Nanocellulose/bioactive glass cryogels as scaffolds for bone regeneration†
Abstract
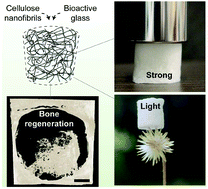
A major challenge exists in the preparation of scaffolds for bone regeneration, namely, achieving simultaneously bioactivity, biocompatibility, mechanical performance and simple manufacturing. Here, cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) are introduced for the preparation of scaffolds taking advantage of their biocompatibility and ability to form strong 3D porous networks from aqueous suspensions. CNF are made bioactive for bone formation through a simple and scalable strategy that achieves highly interconnected 3D networks. The resultant materials optimally combine morphological and mechanical features and facilitate hydroxyapatite formation while releasing essential ions for in vivo bone repair. The porosity and roughness of the scaffolds favor several cell functions while the ions act in the expression of genes associated with cell differentiation. Ion release is found critical to enhance the production of the bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) from cells within the fractured area, thus accelerating the in vivo bone repair. Systemic biocompatibility indicates no negative effects on vital organs such as the liver and kidneys. The results pave the way towards a facile preparation of advanced, high performance CNF-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...