Mesoporous N-doped graphene prepared by a soft-template method with high performance in Li–S batteries†
Abstract
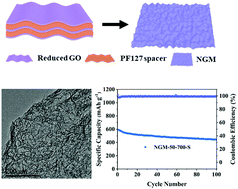
Lithium sulfur (Li–S) batteries, which have high theoretical capacity, are promising candidates for energy storage systems; however, several obstacles, including insulating nature and volumetric expansion of sulfur as well as shuttle effects of polysulfides, impede the commercialization of these batteries. Herein, we utilized mesoporous N-doped graphene (NGM) as a sulfur host, which was synthesized using a type of triblock copolymer, Pluronic F127 (PF127), as a soft template. PF127 not only acted as a spacer to prevent the graphene layers from restacking during the hydrothermal reaction, but also resulted in the formation of high-density wrinkles on the surface of the graphene sheets after annealing. The crumpled NGM with a nitrogen doping content of 4.80 at% had the high specific area and total pore volume of up to 958.72 m2 g−1 and 2.39 cm3 g−1, respectively, providing space for the accommodation and uniform distribution of sulfur in the cathode. Therefore, the sulfur content was increased to 87.2 wt% in the graphene sulfur composite, achieving the discharge capacity of 492.2 mA h g−1TE at 1.08 A g−1TE with a low capacity decay rate of 0.12% per cycle after 400 cycles. Thus, this study provides an effective strategy for enhancing the specific surface area and pore volume of graphene to develop Li–S batteries with high performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...