Stiffness tomography of eukaryotic intracellular compartments by atomic force microscopy†
Abstract
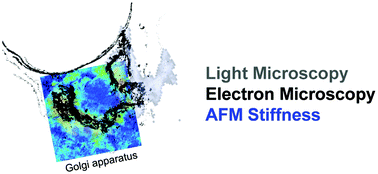
Precise localization and biophysical characterization of cellular structures is a key to the understanding of biological processes happening both inside the cell and at the cell surface. Atomic force microscopy is a powerful tool to study the cell surface – topography, elasticity, viscosity, interactions – and also the viscoelastic behavior of the underlying cytoplasm, cytoskeleton or the nucleus. Here, we demonstrate the ability of atomic force microscopy to also map and characterize organelles and microorganisms inside cells, at the nanoscale, by combining stiffness tomography with super-resolution fluorescence and electron microscopy. By using this correlative approach, we could both identify and characterize intracellular compartments. The validation of this approach was performed by monitoring the stiffening effect according to the metabolic status of the mitochondria in living cells in real-time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...