Development of fluorescent nanoparticles with aggregation-induced delayed fluorescence features, improved brightness and photostability for living cells imaging†
Abstract
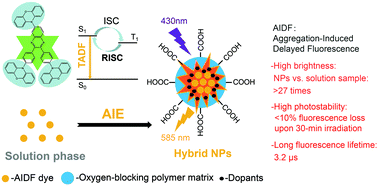
Novel hybrid fluorescent nanoparticles (NPs) characterized with salient features of fluorescence brightness, photostability and fluorescence lifetime were fabricated based on fluorescent dyes (DBQ-3PXZ) with thermal activation delayed fluorescence (TADF) and aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics (aggregation-induced delayed fluorescence, AIDF). An amphiphilic polymer with oxygen-blocking properties was used as the host matrix, while small-molecular-weight antifade agents (singlet oxygen quencher and antioxidant) and a triplet energy barrier were incorporated in the hybrid NPs. The matrix polymer, which is capable of separating DBQ-3PXZ molecules from molecular oxygen, and the incorporated antifade agents, which are capable of suppressing the oxygen-mediated photodegradation of DBQ-3PXZ, contributed to the excellent photostability of the target hybrid NPs. The intrinsic AIE properties and the triplet energy barrier capable of confining the triplet excitons within the dye molecules jointly enabled the high fluorescing ability of DBQ-3PXZ dyes residing in the core part of the NPs. Additionally, the TADF nature of DBQ-3PXZ dye together with the protective role of the matrix polymer and antifade agents imparted long fluorescence lifetimes to the target NPs. The preliminary cell fluorescence imaging results verified the practicability of these feature-packed NPs for highlighting regions of interest and enabling high-resolution visualization of fine subcellular architectures; this unequivocally proclaims this probe to be an ideal tag for biological fluorescence imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...