Synthesis of diarylidenecyclohexanone derivatives as potential anti-inflammatory leads against COX-2/mPGES1 and 5-LOX†
Abstract
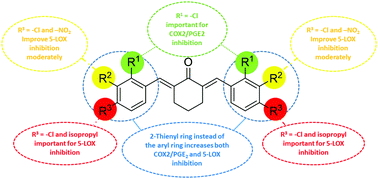
Inflammation is a pathophysiological condition which progresses through the prostaglandin (PG) and leukotriene (LT) pathways channelized by the enzymes COX/mPGES1 and 5-LOX respectively. Diarylidenecyclohexanone (DAC) derivatives (Ia–j, IIa–c, IIIa and IVa) were synthesized, characterized and screened for their in vitro anti-inflammatory activity via inhibition of 5-LOX and COX-2/mPGES1 enzymes. Compound Ic inhibited PGE2 production exhibiting an IC50 of 6.7 ± 0.19 μM, comparable to the standard inhibitor, licofelone (IC50 of 5.4 ± 0.02 μM). Compounds Ie and Ig showed maximum in vitro inhibitory activity against 5-LOX, exhibiting an IC50 of 1.4 ± 0.1 μM and 1.5 ± 0.13 μM, respectively, and these are comparable to that of the standard drug, zileuton (IC50 = 1.2 ± 0.11 μM). Ie and Ig do not possess radical scavenging properties and may not be disrupting the redox cycle of the enzyme. Hence they may be inhibiting the enzyme by a competitive mode. One of the compounds in the DAC series (IIc) containing a heterocyclic thienyl ring inhibited all the three enzymes. It inhibited 5-LOX and COX-2/mPGES1 with an IC50 of 1.8 ± 0.12 μM and 7.5 ± 0.4 μM respectively. An RT-PCR based mRNA expression study highlighted that Ic predominantly inhibited the expression of COX-2 rather than mPGES1. No toxicity towards the HeLa cell line indicated that the DACs could serve as structural templates towards lead optimization of compounds for discovery of novel, potent, safe and affordable drugs as anti-inflammatory agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...