Synthesis of microporous silica nanoparticles to study water phase transitions by vibrational spectroscopy†
Abstract
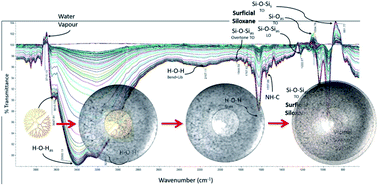
Silica can take many forms, and its interaction with water can change dramatically at the interface. Silica based systems offer a rich tapestry to probe the confinement of water as size and volume can be controlled by various templating strategies and synthetic procedures. To this end, microporous silica nanoparticles have been developed by a reverse microemulsion method utilizing zinc nanoclusters encapsulated in hydroxyl-terminated polyamidoamine (PAMAM-OH) dendrimers as a soft template. These nanoparticles were made tunable within the outer diameter range of 20–50 nm with a core mesopore of 2–15 nm. Synthesized nanoparticles were used to study the effects of surface area and microporous volumes on the vibrational spectroscopy of water. These spectra reveal contributions from bulk interfacial/interparticle water, ice-like surface water, liquid-like water, and hydrated silica surfaces suggesting that microporous silica nanoparticles allow a way to probe silica water interactions at the molecular scale.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...