Relationship between structure and molecular interactions in monolayers of specially designed aminolipids†
Abstract
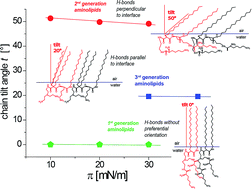
Artificial cationic lipids are already recognized as highly efficient gene therapy tools. Here, we focus on another potential use of aminolipids, in their electrically-uncharged state, for the formation of covalently cross-linked, one-molecule-thin films at interfaces. Such films are envisioned for future (bio-)materials applications. To this end, Langmuir monolayers of structurally different aminolipids are comprehensively characterized with the help of highly sensitive surface characterization techniques. Pressure-area isotherms, Brewster angle microscopy, grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection–absorption spectrometry experiments provide a detailed, comparative molecular picture of the formed monolayers. This physico-chemical study highlights the relationship between chemical structures and intermolecular interactions, which can serve as a basis for the rational design of cross-linked thin films with precisely controlled properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...