Extracting structural information of Au colloids at ultra-dilute concentrations: identification of growth during nanoparticle immobilization†
Abstract
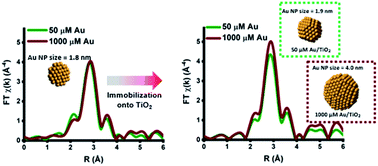
Sol-immobilization is increasingly used to achieve supported metal nanoparticles (NPs) with controllable size and shape; it affords a high degree of control of the metal particle size and yields a narrow particle size distribution. Using state-of-the-art beamlines, we demonstrate how X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) techniques are now able to provide accurate structural information on nano-sized colloidal Au solutions at μM concentrations. This study demonstrates: (i) the size of Au colloids can be accurately tuned by adjusting the temperature of reduction, (ii) Au concentration, from 50 μM to 1000 μM, has little influence on the average size of colloidal Au NPs in solution and (iii) the immobilization step is responsible for significant growth in Au particle size, which is further exacerbated at increased Au concentrations. The work presented demonstrates that an increased understanding of the primary steps in sol-immobilization allows improved optimization of materials for catalytic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...