Optimizing linear polymer affinity agent properties for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of aflatoxin B1†
Abstract
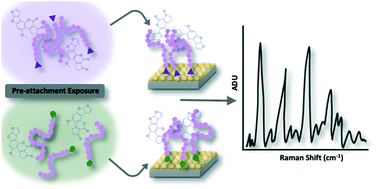
A series of poly(N-acryloyl glycinamide) (pNAGA) polymers were synthesized and studied as capture agents for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) detection of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), a highly carcinogenic food-borne toxin. Four molecular weights of pNAGA were synthesized by reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization to study the dependence of affinity agent efficacy on chain length for this AFB1 sensing platform. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) was used to verify the sign and magnitude of the enthalpic effects involved in polymer–AFB1 interactions in solution and to understand the effects of pNAGA chain length on AFB1 noncovalent binding. pNAGA–AFB1 interactions were found to be exothermic, and longer pNAGA chains generally resulted in smaller enthalpy decreases per repeat unit. With pNAGA22 being thermodynamically the strongest affinity agent, we hypothesize that AFB1 affinity is determined by a balance between the configurational restrictions in pNAGA chains and the enthalpic advantage of binding AFB1. SERS spectral changes observed following AFB1 exposure were used to evaluate the influence of polymer molecular weight (2.0–5.2 kDa), order of attachment (pre- vs. post- functionalization of the substrate) and attachment chemistry (thiol vs. trithiocarbonate) on the sensitivity of AFB1 detection. The method by which target, polymer affinity agent, and signal transduction mechanism are combined was found to have significant impacts on the achieved sensitivity. The most effective polymer chain length (pNAGA22), anchoring chemistry (thiol), and polymer/toxin assembly scheme (in-solution) allowed detection of 10 ppb AFB1 in water (below the FDA regulatory limit of 20 ppb), a hundred-fold improvement over SERS sensing without the pNAGA affinity agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...