A cell-based screening system for RNA polymerase I inhibitors†
Abstract
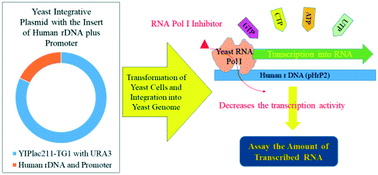
RNA polymerase I (RNA Pol I) is a “factory” that orchestrates the transcription of ribosomal RNA for constructing ribosomes as a primary workshop for protein translation to sustain cell growth. The deregulation of RNA Pol I often causes uncontrolled cell proliferation, leading to cancer. Efficient and reliable methods are needed for the identification of selective inhibitors of RNA Pol I. Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is eukaryotic and represents a valuable model system to study RNA Pol I, especially with the availability of the X-ray crystal structure of the yeast homologue of RNA Pol I, offering a structural basis to selectively target this transcriptional machinery. Herein, we developed a cell-based screening strategy by establishing a stable yeast cell line with a stably integrated human RNA Pol I promoter and ribosomal DNA. The model system was validated using the well-known RNA Pol I inhibitor CX-5461 by measuring transcribed human rRNA as readout. Virtual screening coupled with compound library screening using this cell line enabled the identification of a new candidate inhibitor of RNA Pol I, namely, cerivastatin sodium. Furthermore, we used growth and transcription activity assays to biologically evaluate the hit compound. Preliminary studies demonstrated antiproliferative effects of cerivastatin sodium against human cancer cells, namely, A2780 and H460 cell lines. These results implicated cerivastatin sodium as a selective RNA Pol I inhibitor worthy of further development together with potential as a targeted anticancer therapeutic.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...