Selective modulation of the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor as an emerging platform for the treatment of neuropathic pain
Abstract
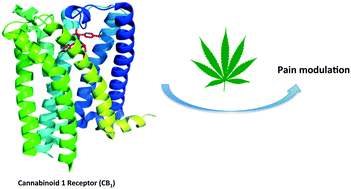
Neuropathic pain is caused by a lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system, and it may arise from illness, be drug-induced or caused by toxin exposure. Since the discovery of two G-protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) nearly three decades ago, there has been a rapid expansion in our understanding of cannabinoid pharmacology. This is currently one of the most active fields of neuropharmacology, and interest has emerged in developing cannabinoids and other small molecule modulators of CB1 and CB2 as therapeutics for neuropathic pain. This short review article provides an overview of the chemotypes currently under investigation for the development of novel neuropathic pain treatments targeting CB1 receptors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...