Bioaccessibility and biotransformation of anthocyanin monomers following in vitro simulated gastric-intestinal digestion and in vivo metabolism in rats
Abstract
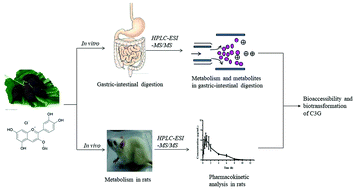
Anthocyanins (ANCs) are phytochemicals with several health effects and undergo significant degradation and subsequent biotransformation during complex metabolic processes. The aim of the present study was to determine the bioaccessibility and biotransformation of cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G) during the simulated gastric-intestinal digestion in vitro and the metabolism in rats in vivo. Characterization of C3G and its metabolites was conducted by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. After gastric-intestinal digestion, C3G was detected with a recovery of 88.31% in the gastric-digestive system, and a small amount of methylated-C3G occurred. In the intestinal-digestive system, C3G occurred with a recovery of 6.05%, and mainly decomposed into protocatechuic acid (PCA) and 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde. The pharmacokinetic trial of C3G in rats showed rapid elimination in plasma. In tissues, C3G underwent rapid absorption and metabolism into phenolic acids or their derivatives. C3G and methylated-C3G passed through the blood–brain barrier and caused rapid distribution of C3G in the brain. Understanding the conversion of C3G and its metabolites helps in the future design of dietary interventions and the exploration of biological activities of ACNs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...