Mono- and ditopic hydroxamate ligands towards discrete and extended network architectures†
Abstract
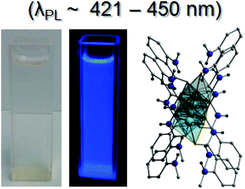
A family of mono- and ditopic hydroxamic acids has been employed in the synthesis and structural and physical characterisation of discrete (0D) and (1- and 2-D) extended network coordination complexes. Examples of the latter include the 1-D coordination polymer {[Zn(II)(L3H)2]·2MeOH}n (5; L3H2 = 2-(methylamino)phenylhydroxamic acid) and the 2-D extended network {[Cu(II)(L2H)(H2O)(NO3)]·H2O}n (5; L2H2 = 4-amino-2-(acetoxy)phenylhydroxamic acid). The 12-MC-4 metallacrown [Cu(II)5(L4H)4(MeOH)2(NO3)2]·3H2O·4MeOH (7) represents the first metal complex constructed using the novel ligand N-hydroxy-2-[(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl)amino]benzamide (L4H3). Variable temperature magnetic susceptibility studies confirm strong antiferromagnetic exchange between the Cu(II) centres in 7. Coordination polymer 5 shows photoluminescence in the blue region (λPL ∼ 421–450 nm) with a bathochromic shift of the emission (∼15–30 nm) from solution to the solid state.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...