The role of methylation in the copper(ii) coordination properties of a His-containing decapeptide†
Abstract
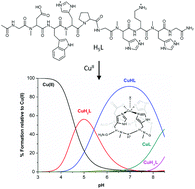
N-Methylation of the peptide amide bond has proven to be a powerful strategy to fine-tune the conformation and properties of peptides. In this context and for the first time, we show that N-methylation can also be used to control the copper(II) coordination properties of peptides and stabilize at high pH values the copper(II) species lacking amidate coordination. Namely, we have prepared a derivative of the O-Asp peptide where the copper(II) coordinating amino acids, i.e. Asp and His residues, were N-methylated (ONMe-Asp). A combined study using potentiometric and spectroscopic (UV-Vis, CD, EPR and NMR) techniques indicates the formation of the wanted major species, [CuH(ONMe-Asp)]2+, where copper(II) is bound to His4(Nε), His7(Nε), His9(Nε) and Asp2(COO−). With respect to the parent non-methylated O-Asp peptide, [CuH(ONMe-Asp)]2+ is stable at higher pH values but has lower affinity for copper(II). Additionally, electrochemical studies reveal a Cu(II) ⇌ Cu(I) redox process with a larger cathodic and anodic peak separation. Species containing copper(II) coordinating amidates were not observed for this ONMe-Asp peptide.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...