Dansyl-appended CuII-complex-based nitroxyl (HNO) sensing with living cell imaging application and DFT studies†
Abstract
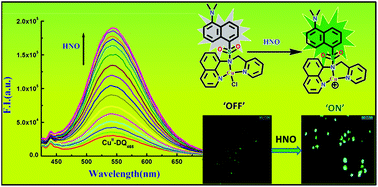
We introduce herein, a novel copper complex-based fluorescent probe [CuII(DQ468)Cl]+ that exhibits a significant fluorescence turn-on response towards nitroxyl (HNO) with high selectivity over other biological reactive oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur species, including nitric oxide (NO). A smart strategy, involving HNO-induced reduction of paramagnetic [CuII(DQ468)Cl]+ to diamagnetic [CuI(DQ468)]+ with concomitant fluorescence enhancement via a PET mechanism is focused here. This reduction-based strategy was also supported by X-band EPR response and mass spectroscopy. The metal free probe (DQ468) showed high affinity towards Cu2+ to form [CuII(DQ468)Cl]+ with a 0.091 μM detection limit, which subsequently enabled the detection of HNO in an organo-aqueous medium at biological pH (7.4) in the green wavelength region (λem = 543 nm) with a LOD of 0.41 μM. The ground-state geometries of DQ468, [CuII(DQ468)Cl]+ and [CuI(DQ468)]+ were optimized by DFT calculations, which revealed that the central metal ion in [CuII(DQ468)Cl]+ is in a distorted tetrahedral geometry with the C1 point group. Additionally, the negligible cytotoxicity and good biocompatibility make the developed probe useful for the in vitro detection of HNO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...