Site-selective Ru-catalyzed C–H bond alkenylation with biologically relevant isoindolinones: a case of catalyst performance controlled by subtle stereo-electronic effects of the weak directing group†
Abstract
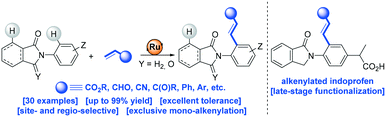
The first use of biologically relevant isoindolinones as weak directing groups in transition metal-catalyzed carbon–carbon bond formation via C–H bond functionalization is presented. Notably, besides the presence of two aromatic C–H sites available for functionalization, selective mono-alkenylation in the ortho-position with respect to the nitrogen atom were achieved with a readily available ruthenium catalyst. The scalability, versatility and high functional group tolerance of the catalysis enabled the late-stage functionalization of biologically relevant indoprofen and further derivatizations. Preliminary mechanistic studies indicate (1) the ease of the C–H bond activation step, (2) the key role of the carbonyl group as a weak directing group throughout the catalytic cycle and (3) the unexpected subtle differences associated between cyclic amides and imides as weak directing groups in ruthenium-catalyzed C–H bond alkenylation reactions. The isolation and role of an unprecedented off-cycle ruthenium complex is discussed as well.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...