Extending the temperature sensing range using Eu3+ luminescence up to 865 K in a single crystal of EuPO4†
Abstract
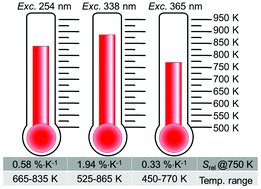
Temperature evaluation through the measurement of emission intensities (the intensity ratio method) requires two distinct bands, one of which is used as a reference, and the emission intensity of the other is monitored as a function of a change in temperature. Herein, we report the influence of the excitation wavelength and a coupling scheme between the lanthanoid and defect emission from the host lattice to extend the temperature sensing range by using a single crystal of europium(III) phosphate. The temperature dependence of the emission intensity was studied for different excitation wavelengths: 365 (intraconfigurational 4f2 excitation), 338 (defect excitation), and 254 nm (O2− → Eu3+ charge-transfer excitation), in the temperature range 293–865 K. We determined the Boltzmann equilibrium among different coupling schemes using a linear regression model to infer that for excitation at a 338 nm wavelength, and evaluating the intensity ratio between defect emission and the Eu3+ 5D0,17FJ transitions, the temperature sensing range can be extended up to at least 865 K, with relative sensitivity in the range 0.33–1.94% K−1 (at 750 K). The results showed a resolution of <1 K with excellent reproducibility, suggesting that the thermometers can be used with high reliability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...