A new type of halogen bond involving multivalent astatine: an ab initio study†
Abstract
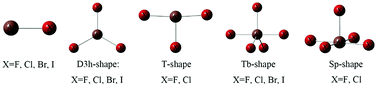
Theoretical studies on the dimers formed by CO with the halides of multivalent astatine as a Lewis-acid center are carried out to examine the typical characteristics of supervalent halogen bonds. Calculations at the MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ level reveal that the multiple nucleophilic sites of multivalent halide monomers can promote the formation of various types of halogen bonds, among which the most stable ones are At–halogen bond complexes with multivalent astatine as a Lewis acid center, followed by the π–halogen bond dimers, and the weakest ones are the X–halogen bonds. Compared with multivalent Cl-, Br-, and I-centers, At, as the heaviest halogen, exhibits the highest halogen-bond donating ability. We found that the electrostatic term and the dispersion term play an important role in the overall attractive interaction energy, and the smallest attraction term for all complexes is the polarization term (ΔEpol). Moreover, the tri and pentavalent halides analyzed here possess very “flexible” tautomerism in which the transformation occurs during the formation of the dimers. AIM theory and NBO analysis are also employed here.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...