Solvent viscosity-dependent isomerization equilibrium of tetramethoxy-substituted bianthrone†
Abstract
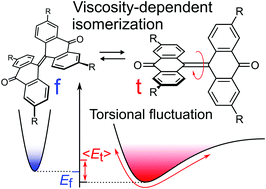
The designed and synthesized tetramethoxy-substituted bianthrone exists as an equilibrium mixture of the folded and twisted conformers in solution. The introduction of methoxy groups into the 3,3′,6,6′-positions of bianthrone reduces the energy difference between the conformers and results in a bistable system. The survey of its equilibrium constant based on the optical absorption and variable temperature quantitative NMR spectroscopic studies in various solvents revealed that the equilibration of the isomerization reaction was found to be most sensitive to solvent viscosity among various solvent parameters. In the statistical thermodynamic approach combined with DFT calculations, the twisted conformations with various torsional angles are populated by thermal fluctuations on the highly anharmonic potential surface, and their ensemble average depends on solvent viscosity because a viscous drag of the solvent controls the degree of fluctuation. Such a statistical population does not occur in the folded conformer because of the harmonic potential surface with respect to the torsional rotation. This difference may result in the solvent viscosity dependence of the isomerization equilibrium constant, that is, the energy difference between the conformers.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...