Stereochemical effects on the mechanochemical scission of furan–maleimide Diels–Alder adducts†
Abstract
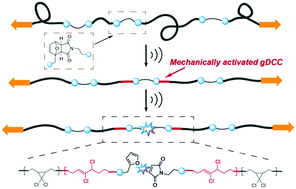
Clarifying the correlation between the chemical structure of mechanophores and their mechanical reactivity informs the design of mechanochemical systems. One specific correlation that has received much recent attention is that between stereoisomerism and mechanical reactivity. Here, we report previously unobserved differences in the mechanical reactivity of furan–maleimide Diels–Alder (DA) stereoisomers. We evaluated the internal competition between the mechanically triggered retro-DA reaction and the mechanochemical ring opening of gem-dichlorocyclopropane mechanophores in the pulsed sonication of polymer solutions. The relative extent of the two sonomechanochemical reactions in the same polymer shows that the endo DA isomer exhibits greater mechanical lability than its exo isomer. This result contrasts with recent measurements of the relative rates of scission in a similar system and points to potential enhanced sensitivity obtained through the use of internal competition as opposed to absolute rates in assessing mechanical reactivity in sonication studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...