Enhanced drug internalization and therapeutic efficacy of PEGylated nanoparticles by one-step formulation with anti-mPEG bispecific antibody in intrinsic drug-resistant breast cancer†
Abstract
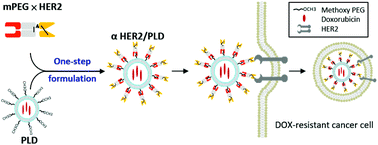
For those patients with HER2-overexpressing breast cancer, treatment with PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) is inefficacious due to the intrinsic low sensitivity to doxorubicin. A very large increase in drug accumulation by active targeting may enhance the therapeutic efficacy of PLD. We established a humanized bispecific antibody (BsAb; mPEG × HER2) which has dual specificity for methoxy-polyethylene glycol (mPEG) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) to enhance the specificity, internalization and anticancer activity of PLD for cancer cells that overexpress HER2. One-step formulation of PLD with mPEG × HER2 converted the PLD into HER2 targeted liposomes that were stable at 4 °C in PBS as well as at 37 °C in the presence of serum. αHER2/PLD induced receptor-mediated endocytosis and enhanced doxorubicin accumulation in MCF7/HER2 (HER2-amplified) breast cancer cells. αHER2/PLD also displayed more than 200-fold increased cytotoxicity to MCF7/HER2 cells and 28-fold increased cytotoxicity to drug-resistant MDA-MB-361 cells with a physical deletion of the TOP2A gene. αHER2/PLD specifically accumulated doxorubicin in the nucleus of cancer cells in tumor-bearing mice and produced significantly greater antitumor activity against MCF7/HER2 (P < 0.0001) and MDA-MB-361 (P < 0.05) tumors as compared to untargeted PLD. Furthermore, the cardiotoxicity of αHER2/PLD was similar to that of PLD in human cardiomyocytes and in mice. Our results indicate that the one-step formulation of PLD by mPEG × HER2 is a simple method to confer tumor specificity, increase drug internalization and enhance the anticancer activity of PLD against HER2-overexpressing and doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...