A polyethylenimine-based diazeniumdiolate nitric oxide donor accelerates wound healing
Abstract
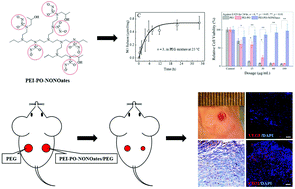
Nitric oxide (NO) plays a pivotal role in the cutaneous healing process and a topical supplement of NO is beneficial for wound repair. In this work, a novel polyethylenimine (PEI) based diazeniumdiolate nitric oxide donor was prepared. The obtained polymer (PEI-PO-NONOate) was characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, UV-vis absorption spectra, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The PEI-PO-NONOate polymer was stable under anhydrous conditions at different temperatures. A total of 0.57 μmol gaseous NO was released from 1.0 mg of the PEI-PO-NONOate polymer in PBS of pH 7.4 and it presented a proton-driven release pattern. Furthermore, the PEI-PO-NONOate polymer exhibited a controlled release profile sustained for over 30 hours within the polyethylene glycol (PEG) mixture system. Cytotoxicity evaluation was performed on L929 cells. Full-thickness excisional cutaneous wound models of mice were prepared and the PEI-PO-NONOate polymer was applied to investigate its effects on wound healing. The results revealed that the PEI-PO-NONOates exhibited good biocompatibility. It was also found that the PEI-PO-NONOate polymer promoted cutaneous wound healing and closure with enhanced granulation tissue formation, collagen deposition, and angiogenesis, as compared to the control. In summary, a novel nitric oxide releasing polymer with high loading efficiency and a controlled release profile was developed which presented the potential for application in the acceleration of cutaneous wound healing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...