Feasibility study for rapid near-infrared spectroscopic identification of different gallbladder diseases by direct analysis of bile juice
Abstract
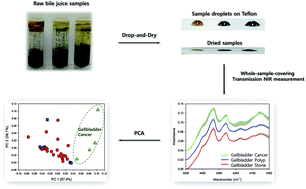
A whole-sample-covering near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy scheme has been adopted for the simple drop-and-dry measurement of raw bile juice for the identification of gallbladder (GB) diseases of stone, polyp, and cancer. For reproducible measurement, a non-NIR absorbing polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) providing a hydrophobic surface was chosen as a substrate to form bile juice droplets of a consistent shape. To ensure representative spectroscopic sampling, NIR radiation illuminated the whole area of the dried sample for spectral acquisition. The NIR band shapes and relative band intensities of GB cancer differed moderately from those of GB stone and GB polyp. The composition of GB cancer samples was presumed to be dissimilar from other sample compositions. Differentiation between GB polyp and GB stone, however, was less facile; nevertheless, in the case of GB polyp samples, the obtained NIR features were informative in the identification of various pathological conditions such as adenomyomatosis (abnormal growth of epidermal tissue) and hepatitis B. To elucidate the NIR features of bile juice samples, separate NIR spectra of major bile constituents such as conjugated bile salts, lecithin, cholesterol, and albumin were analyzed. The demonstrated NIR spectroscopy scheme requiring no sample pretreatment or separation of bile juice could be useful for fast bile juice-based screening of GB diseases, especially the identification of early GB cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...