Responsive surface bioaffinity binding to construct flexible and sensitive electrochemical aptasensors†
Abstract
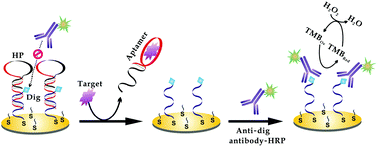
The development of simple, flexible, cost-effective and sensitive electrochemical biosensing strategies is highly desirable to advance their applications in disease diagnostics and clinical biomedicine. Herein, we fabricated a new enzyme-based electrochemical aptasensor with the use of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and thrombin as model targets on the basis of a responsive surface bioaffinity binding strategy. It took full advantage of an immobilized complex duplex probe (hybrids of a hairpin-like aptamer probe with a digoxigenin (Dig)-labeled immobilization strand) to effectively inhibit the approach of the bulky horseradish peroxidase linked-anti-Dig antibody (anti-Dig-HRP) to the Dig on the electrode due to the steric effect. The target recognition dissociated the aptamer strand from the duplex probe and exposed the Dig for its effective binding with anti-Dig-HRP. The successive electrocatalysis offered a significantly amplified electrochemical signal correlated with the target recognition event. Sensitive detection toward ATP and thrombin was achieved with detection limits of 0.87 nM and 6.3 pM, respectively. The proposed strategy is simple and sensitive without any complex operations that hinder many amplified aptasensors. Also, the target recognition and signal reporting units are relatively isolated, making the biosensor fabrication more flexible. It thus provided a new and versatile pathway for sensitive biosensor fabrication.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...