Perinatal exposure to 4-nonylphenol can affect fatty acid synthesis in the livers of F1 and F2 generation rats†
Abstract
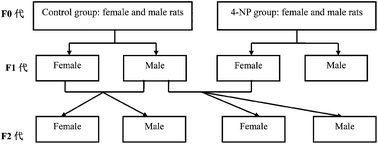
Objective: To explore the effects of different dosages of 4-nonylphenol (4-NP) on the fatty acid synthesis and estrogen receptor α (ERα) expression in the livers of F1 and F2 rats. Method: Pregnant rats were randomly divided into four groups: control, NP-5 (5 μg per kg per day), NP-25 (25 μg per kg per day) and NP-125 (125 μg per kg per day). 4-NP was gavaged from gestation day (GD) 6 to postnatal day (PND) 21. Some female rats from the experimental groups were mated with male rats from the control group to obtain the F2 rats. F1 generation rats (23 weeks old) and F2 generation rats (13 weeks old) were killed to detect blood biochemistry and the expression of genes and proteins. Results: Compared with the control group, 4-NP (NP-5, NP-25 and NP-125) can increase the liver organ coefficient of the F1 male offspring (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The concentration of high density lipoprotein (HDL) in the F1 female NP-5 group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P < 0.01); other indicators had not changed, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total cholesterol (TC) and low density lipoprotein (LDL). As the dosage of 4-NP increased, more significant changes of blood biochemistry were found, especially in the NP-125 rats (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The changes of histopathology by liver biopsy were consistent with biochemical indices of blood (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Compared with the control group, the expression of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis increased significantly (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), and the degrees of increase were proportional to the dose of 4-NP, as measured by lipoprotein lipase (Lpl), fatty acid synthetase (Fas), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (Srebp-1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (Ppar)-γ. The expression of genes and proteins of ERα were changed significantly, as well (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The above changes in the liver tissues of F2 generation rats were consistent with the F1 generation rats. Conclusion: Perinatal exposure to 4-NP can affect the synthesis of fatty acid in the livers of F1 and F2 generation rats. The low expression of ERα may be one of the mechanisms by which 4-NP affected fatty acid synthesis in the livers of rats.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...