Emodin induces liver injury by inhibiting the key enzymes of FADH/NADPH transport in rat liver†
Abstract
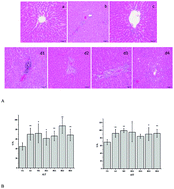
Emodin is a natural anthraquinone derivative that occurs in many Chinese medicinal herbs. It might induce liver damage, but the mechanism is not clear. In this research, seven groups of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats with three doses of emodin were used. The liver injury was examined by analyzing biochemical indexes and histopathology. Altered proteins between the control group (CG) and the liver injury group were determined by proteomic technology. The results showed that emodin causes liver injury in a time- and dose-dependent manner. In the high-dosage 1-week group (HG1), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was downregulated, and the activity of malate dehydrogenase (MDH) was inhibited by emodin. These might cause the inhibition of FADH or NADH/NADPH transport from the cytoplasm to mitochondria. The WB results showed that the inhibition of FADH/NADPH transport induced a high activity of caspase-9 and caspase-3, and the expressions of cytochrome c (Cyt C), caspase-9 and caspase-3 were high in HG1, which might lead to mitochondrial apoptosis pathway activation. In addition, whatever the HG1 or low-dose group (LG), the effects of emodin on mitochondria were observed. Overall, for the first time, we showed that emodin inhibited proton transport and induced the activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway, which might be the reason for liver injury.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...