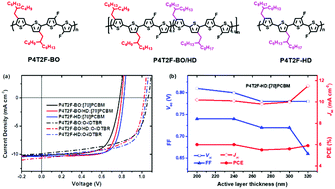
In this work we report three novel polythiophene derivatives (P4T2F-HD, P4T2F-HD/BO, and P4T2F-BO) which are synthesized via a three-step reaction in each case. The polymers show excellent coplanarity and desired aggregation characteristics in solution. The HOMO energy levels of the new polymers were down-shifted by 0.4 eV as compared to the commercial polymer poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT). The polymers are able to offer high device performance when combined with both fullerene and non-fullerene acceptors. When blended with a non-fullerene acceptor (5Z,5′Z)-5,5′-(((4,4,9,9-tetraoctyl-4,9-dihydro-s-indaceno[1,2-b:5,6-b′]dithiophene-2,7-diyl)bis(benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-7,4-diyl))bis-(methanylylidene))bis(3-ethyl-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one) (O-IDTBR), P4T2F-HD offers the highest PCE of 7.0% with a high Voc of 1.04 V. Moreover, P4T2F-HD can tolerate the variation of active layer thickness over a large range when blended with a fullerene acceptor. The decent device performance and processability under mild conditions demonstrate that polythiophene derivatives hold great potential for application in large-scale production of polymer solar cell modules.