Temperature sensitive cross relaxation between Er3+ ions in laminated hosts: a novel mechanism for thermochromic upconversion and high performance thermometry†
Abstract
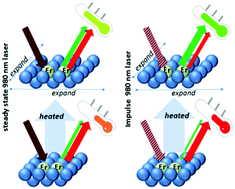
This work demonstrates a novel mechanism of temperature sensitive upconversion luminescence. The Yb/Er:La2MoO6 phosphor is taken as a typical example. The laminated lattice structure of the La2MoO6 host endows a high potential of the 4F7/2 + 4I11/2 → 4F9/2 + 4F9/2 cross relaxation of the Er3+ dopant. It is found that such cross relaxation is sensitive to the variation of temperature, resulting in a distinct variation in fluorescence intensity ratio and thus a remarkable thermochromic upconversion luminescence. Employing this material as an optical thermometer, the maximum relative sensitivity is calculated to be 1.6% K−1 at room temperature, which is superior to most of the Er based thermometers reported previously. In addition, when an impulse pump is utilized, the maximum sensitivity can be further enhanced up to 3.3% K−1. The anisotropic thermal expansion of the La2MoO6 host lattice is proposed to be responsible for such temperature dependent luminescence. Other hosts (i.e. LaOCl and BiOCl) with similar laminated lattice structures have also been investigated, which exhibit a similar temperature sensing property. This work not only presents a novel strategy for constructing upconversion thermometric materials, but also provides inspiration that developing impulse excited optical thermometric materials might be a promising route for the field of temperature sensing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...