Ultraviolet electroluminescence from a n-ZnO film/p-GaN heterojunction under both forward and reverse bias
Abstract
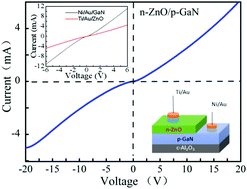
ZnO film was fabricated on p-GaN film using the molecular beam epitaxy technique to form heterojunction light emitting diodes (LEDs). The devices exhibited strong light emission under both forward and reverse bias. The origin of different luminescence peaks has been investigated by comparing electroluminescence (EL) and photoluminescence spectra. When a forward bias is applied to the device, intense ultraviolet emission at ∼376 nm originating from ZnO rather than GaN can be observed, which is associated with the larger hole mobility of p-GaN than the electron mobility of n-ZnO. Under the reverse bias, the device shows broad emission at 520 nm originating from deep level-related recombination in ZnO, emission at 430 nm from GaN, 376 nm from ZnO and weak emission at 408 nm from the interface with a lower injection current of 10 mA. As the injection reverse current increases to 20 mA, the EL emission at 376 nm exhibits a dramatic increase in intensity without a peak shift. The emission mechanism of the heterojunction LED is discussed in terms of interface states and energy band theory. Our findings in this work provide an innovative path for the design and development of ZnO-based ultraviolet diodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...