Colloidal tin sulfide nanosheets: formation mechanism, ligand-mediated shape tuning and photo-detection†
Abstract
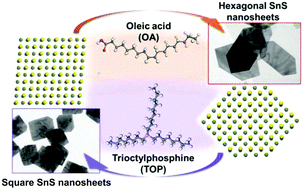
Colloidal materials of tin(II) sulfide (SnS), as a layered semiconductor with a narrow band gap, are emerging as a potential alternative to the more toxic metal chalcogenides (PbS, PbSe, CdS, and CdSe) for various applications such as electronic and optoelectronic devices. We describe a new and simple pathway to produce colloidal SnS nanosheets with large lateral sizes and controllable thicknesses, as well as single-crystallinity. The synthesis of the nanosheets is achieved by employing tin(II) acetate as the tin precursor instead of harmful precursors such as bis[bis(trimethylsilyl)amino] tin(II) and halogen-involved precursors like tin chloride, which limits their large-scale production. We successfully tuned the morphology between squared nanosheets with lateral dimensions from 150 to about 500 nm and thicknesses from 24 to 29 nm, and hexagonal nanosheets with lateral sizes from 230 to 1680 nm and heights ranging from 16 to 50 nm by varying the ligands oleic acid and trioctylphosphine. The formation mechanism of both shapes has been investigated in depth, which is also supported by DFT simulations. The optoelectronic measurements show their relatively high conductivity with a pronounced sensitivity to light, which is promising in terms of photo-switching, photo-sensing, and photovoltaic applications and also due to their reduced toxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...